Family Genogram -Kate Andrews
Family Genogram -Kate Andrews
Learning Objectives
Students will:
- Assess client families presenting for psychotherapy
- Develop genograms for client families presenting for psychotherapy
To prepare:
- Select a client family that you have observed or counseled at your practicum site.
- Reflect on elements of writing a comprehensive client assessment and creating a genogram for the client you selected.
The Assignment
NOTE TO WRITER: You can make up any information in the family client assessment. Be aware that the family was seen for drug addiction during a family therapy session.
Family Genogram -Kate Andrews
Part 1: Comprehensive Client Family Assessment
Create a comprehensive client assessment for your selected client family that addresses (without violating HIPAA regulations) the following:
- Demographic information
- Presenting problem
- History or present illness
- Past psychiatric history
- Medical history
- Substance use history
- Developmental history
- Family psychiatric history
- Psychosocial history
- History of abuse and/or trauma
- Review of systems
- Physical assessment
- Mental status exam
- Differential diagnosis
- Case formulation
- Treatment plan
Part 2: Family Genogram
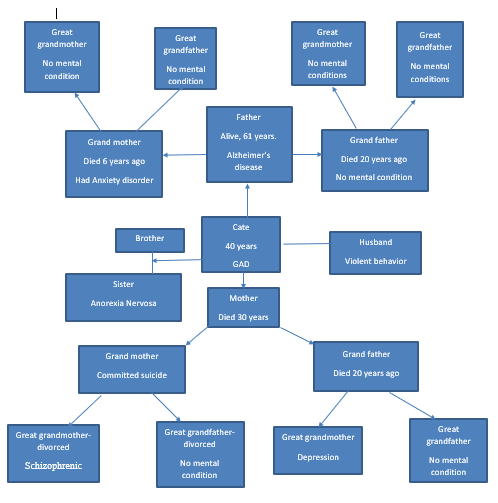
Develop a genogram for the client family you selected. The genogram should extend back at least three generations (parents, grandparents, and great grandparents).
SAMPLE ANSWER
Part 1: Comprehensive Client Family Assessment
Demographics: Kate Andrews is a 40-year-old woman and is married to Bob and is also currently living with her son and her father who has Alzheimer’s disease. She is a devout Christian and works as a teacher in a nearby school. Bob is currently jobless.
Presenting problem: Kate is anxious about life and she complains of insomnia and is easily irritable. Bob, on the other hand, is frustrated about unemployment and hence takes alcohol to calm down
History of present illness: Kate exhibited insomnia and irritability for about four years. Two years ago, a clinician offered antidepressants but she declined and hoped that she would get help from God. Bob has been anxious since he lost his job one year ago.
Family Genogram -Kate Andrews
Past psychiatric history: Kate’s symptoms started a few years into her marriage but became severe when Bob became jobless as he also became violent. She was given antidepressants but did not take them. Bob has not sought any help yet.
Medical history: Kate was offered antidepressants but declined to take them. She has been searching for home remedies online including calming concoctions and some exercises such as yoga; she acknowledges that she needs support to cope. Bob and Kate have no other medical issue.
Substance use history: Kate and Bob indulge in alcohol use to calm down
Developmental history: Kate is the firstborn in a strongly religious family of three children, two girls and a boy. Her mother died when she was about ten years old. She was a healthy child and she exhibited exemplary performance in school. Bob is an only child in their family and also has had a healthy childhood although he experienced domestic violence as a child. Both of his parents are alive and there are no mental issues in his history.
ORDER A PLAGIARISM FREE PAPER HERE
Family psychiatric history: Kate’s grandfather has been diagnosed with depression and her father was at some point diagnosed with an anxiety disorder. Her great-grandmother was schizophrenic. Her grandmother committed suicide and her sister has been diagnosed with an eating disorder. Bob’s father was violent, but there is no other mental history in the family.
Psychosocial history: The family is living with their son and Kate’s father who is suffering from Alzheimer’s disease. They have close friends although Kate also has friends from church who visit and pray with her.
History of abuse/trauma: Bob has been violent and found every reason to beat her up and hurl insults at her since he lost his job. Kate is sad about the state of affairs and is overwhelmed about having to shoulder the responsibilities in the family.
Review of systems
The two look okay generally, there are no major issues. Genrally,l they exhibit malaise and they complain of blurry eyesight. Kate has a sore throat and there is no coughing or wheezing. On musculoskeletal assessment, Bob shows tension in the neck, shoulders, and legs. Psychiatric assessment reveals that there are No thoughts of suicide or hallucinations, although they both exhibit insomnia, and sadness.
Physical assessment: Kate has tension in the neck and shoulders, eyes are red and puffy and Bob looks very tired. Kate has no fever but has lost weight.
Family Genogram -Kate Andrews
Mental status exam: On appearance, Kate has a build posture but exhibits sad emotional expressions. Bob is not well-groomed and has untidy hair and he is unable to maintain eye contact unlike Kate. Kate speaks while taking long pauses although she is fluent. She is conscious and also has memory although she also goes ahead to provide unnecessary information.
Differential diagnosis: although they have substance abuse as the main issue, the differential diagnosis includes Sadness, Adjustment disorder with depressed mood, and Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD. According to Lokko and stern, (2014), sadness occurs when a person exhibits dissatisfaction with life, sorrow, and hopelessness. It presents in different ways and may include insomnia or changes in eating patterns (Bröer, & Besseling, 2017).Casey et al. (2015), define Adjustment disorder with depressed mood as occurring when the patient experiences a change in life which makes them feel overwhelmed. Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) is characterized by a patient showing signs of excessive worry for more than six months (Bui et al .2017).
Case formulation: Kate and Bob both show worry and anxiety about the inability to take care of their son and Kate’s father. Using the metacognitive model, it becomes evident that Kate is worried that she will be unable to meet their needs while Bob is anxious because he is unemployed. The metacognitive model explains by explaining that ruminative thinking makes an individual to repetitively think about the issues that affect a person’s negative emotional experience (Solem, et al. 2016). It, therefore, influences an individual to get worried and this is stored in their long-term memory. Kate and Bob’s worry triggers ruminative thinking and they remember their troubles and consequently think of the recycled thoughts and emotions, which further bring about rumination and the cycle continues. They then indulge in substance use, as a way to help them out of the problem.
Treatment
- Medication, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor to ease the symptoms of depressed mood and anxiety (Ionescu et al. 2015).
- Psychotherapy
Part 2: Kate’s Family Genogram
References
Bröer, C., & Besseling, B. (2017). Sadness or depression: Making sense of low mood and the
Medicalization of everyday life. Social Science & Medicine, 183, 28-36.
Bui, E., Anderson, E., Goetter, E. M., Campbell, A. A., Fischer, L. E., Barrett, L. F., & Simon,
- M. (2017). Heightened sensitivity to emotional expressions in generalized anxiety disorder, compared to social anxiety disorder, and controls. Cognition and Emotion, 31(1), 119-126. doi.org/10.1080/02699931.2015.1087973
Casey, P., Jabbar, F., O’Leary, E., & Doherty, A. M. (2015). Suicidal behaviors in adjustment
Disorder and depressive episode. Journal of affective disorders, 174, 441-446. doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2014.12.003Get rights and content
Ionescu, D. F., Rosenbaum, J. F., & Alpert, J. E. (2015). Pharmacological approaches to the
Challenge of treatment-resistant depression. Dialogues in clinical neuroscience, 17(2), 111–126.
Lokko, H. N., & Stern, T. A. (2014). Sadness: diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment. The primary
Care companion for CNS disorders, 16(6), 10.4088/PCC.14f01709. doi:10.4088/PCC.14f01709
Solem, S., Hagen, R., Hoksnes, J. J., & Hjemdal, O. (2016). The metacognitive model of
Depression: an empirical test in a large Norwegian sample. Psychiatry research, 242, 171-173. doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2016.05.056
Needs help with similar assignment?
We are available 24x7 to deliver the best services and assignment ready within 3-4 hours? Order a custom-written, plagiarism-free paper

