Quality Improvement Initiative Proposal
Quality Improvement Initiative Proposal
In this assessment, you will propose a quality improvement (QI) initiative proposal based on a health issue of professional interest to you. The QI initiative proposal will be based on an analysis of dashboard metrics from a health care facility. You have one of two options:
Option 1
If you have access to dashboard metrics related to a QI initiative proposal of interest to you:
- Analyze data from the health care facility to identify a health care issue or area of concern. You will need access to reports and data related to care quality and patient safety. If you work in hospital setting, contact the quality management department to obtain the data you need.
- You will need to identify basic information about the health care setting, size, and specific type of care delivery related to the topic that you identify. You are expected to abide by HIPAA compliance standards.
Option 2
If you do not have access to a dashboard or metrics related to a QI initiative proposal:
- You may use the hospital data set provided in the media piece titled Vila Health: Data Analysis. You will analyze the data to identify a health care issue or area of concern.
- You will follow the same instructions and provide the same deliverables as your peers who select Option 1.
Instructions
Analyze dashboard metrics related to the selected issue.
- Provide the selected data set in the proposal.
- Assess the stability of processes or outcomes.
- Delineate any problematic variations or performance failures.
- Evaluate QI initiatives on the selected health issue with existing quality indicators from other facilities, government agencies, and non-governmental bodies on quality improvement.
- Analyze challenges that meeting prescribed benchmarks can pose for a heath care organization and the interprofessional team.
- Outline a QI initiative proposal based on the selected health issue and data analysis.
- Identify target areas for improvement.
- Define what processes can be modified to improve outcomes.
- Propose strategies to improve quality.
- Define interprofessional roles and responsibilities as they relate to the QI initiative.
- Provide recommendations for effective communication strategies for the interprofessional team to ensure the success of the QI initiative. Briefly reflect on the impact of the proposed initiative on work-life quality of the nursing staff and interprofessional team.
- Integrate relevant sources to support arguments, correctly formatting citations and references using current APA style.
Note: Remember, you can submit all, or a portion of, your draft to Smarthinking for feedback, before you submit the final version of your analysis for this assessment. However, be mindful of the turnaround time for receiving feedback, if you plan on using this free service.
Quality Improvement Initiative Proposal
The numbered points below correspond to grading criteria in the scoring guide. The bullets below each grading criterion further delineate tasks to fulfill the assessment requirements. Be sure that your Quality Improvement Initiative Evaluation addresses all of the content below. You may also want to read the scoring guide to better understand the performance levels that relate to each grading criterion.
- Analyze data to identify a health care issue or area of concern.
- Identify the type of data you are analyzing (from your institution or from the media piece).
- Discuss why the data matters, what it is telling you, and what is missing.
- Analyze dashboard metrics and provide the data set in the proposal.
- Present dashboard metrics related to the selected issue.
- Delineate any problematic variations or performance failures.
- Assess the stability of processes or outcomes.
- Evaluate the quality of the data and what can be learned from it.
- Identify trends, outcome measures and information needed to calculate specific rates.
- Analyze what metrics indicate opportunities for quality improvement.
- Outline a QI initiative proposal based on a selected health issue and supporting data analysis.
- Identify benchmarks aligned to existing QI initiatives set by local, state, or federal health care policies or laws.
- Identify existing QI initiatives related to the selected issue, and explain why they are insufficient.
- Identify target areas for improvement, and define what processes can be modified to improve outcomes.
- Propose evidence-based strategies to improve quality.
- Evaluate QI initiatives on the selected health issue with existing quality indicators from other facilities, government agencies, and non-governmental bodies on quality improvement.
- Analyze challenges that meeting prescribed benchmarks can pose for a heath care organization and the interprofessional team.
- Integrate interprofessional perspectives to lead quality improvements in patient safety, cost effectiveness, and work-life quality.
- Define interprofessional roles and responsibilities as they relate to the data and the QI initiative.
- Explain how you would you make sure that all relevant roles are fully engaged in this effort.
- Explain what non-nursing concepts would you incorporate into the initiative?
- Identify how outcomes to measure the effect of the intervention affect the interprofessional team.
- Briefly reflect on the impact of the proposed initiative on work-life quality of the nursing staff and interprofessional team. Describe how work-life quality is improved or enriched by the initiative.
- Apply effective communication strategies to promote quality improvement of interprofessional care.
- Identify the kind of interprofessional communication strategies that will be effective to promote and ensure the success of this performance improvement plan or quality improvement initiative.
- In addition to writing, identify communication models (like CUS, SBAR) that you would include in your initiative proposal.
- Communicate evaluation and analysis in a professional and effective manner, writing content clearly and logically with correct use of grammar, punctuation, and spelling.
- Integrate relevant sources to support arguments, correctly formatting citations and references using current APA style.
Quality Improvement Initiative Proposal
Submission Requirements
- Length of submission: 8–10 double-spaced, typed pages, not including title and reference page.
- Number of references: Cite a minimum of five sources (no older than seven years, unless seminal work) of scholarly, peer-reviewed, or professional evidence that support your evaluation, recommendations, and plans.
QUESTIONS TO CONSIDER:
As you prepare to complete this assessment, you may want to think about other related issues to deepen your understanding or broaden your viewpoint. You are encouraged to consider the questions below and discuss them with a fellow learner, a work associate, an interested friend, or a member of your professional community. Note that these questions are for your own development and exploration and do not need to be completed or submitted as part of your assessment.
Reflect on QI initiatives focused on measuring and improving patient outcomes with which you are familiar.
- How important is the role of nurses in QI initiatives?
- What quality improvement initiatives have made the biggest difference? Why?
- When a QI initiative does not succeed as planned, what steps are taken to improve or revise the effort?
SAMPLE ANSWER
Quality Improvement Initiative Proposal
Introduction
The increasing concern about patient safety and reducing adverse events in healthcare have led to more focus being directed towards initiatives that improve quality. In the past, QI initiatives have failed to get support from all healthcare professionals and as a result, have faltered to create permanent change. Many healthcare professionals report resistance when QI initiatives are introduced. To reduce resistance and ensure success, QI initiatives must engage all healthcare providers in all the developmental stages (White, Butterworth & Wells, 2017). Medical errors are at the center of factors that affect quality of care and threaten patient safety. However, with the increasing prominence of electronic health records, many healthcare facilities are using new tools to reduce risks of errors. The proposal will provide a quality improvement initiative to reduce preventable medical errors and infection rates in the ICU department at Virginia Commonwealth University Health System (VCUHS). Data will be obtained from the facility’s clinical dashboard metrics.
About the facility
VCUHS is a Level one trauma center located in Richmond, Virginia. The facility provides care to a population of over 1.2 million individuals since it is the only level one trauma center in the Central Virginia region. With a vision of improving quality, safety and effectiveness of care, the facility has invested in technological systems and tools that facilitate the transformation of clinical practice (VCUHealth, 2019). The Critical Care Hospital at VCU Medical Center is equipped with the latest technology including advanced monitoring devices and mechanical ventilators. Some of the intensive care units at the Critical Care Hospital include; the neuroscience ICU, cardiac surgery ICU, coronary ICU, surgery trauma ICU and the Medical respiratory ICU (VCUHealth, 2019). However, between the years of 2006 and 2008, there were nearly one million patient safety lapses among Medicare patients. As a result, over 100,000 deaths were recorded and excess costs amounting to 8.9 billion USD were incurred. With these numbers in the mind, the facility’s management announced a new safety vision to help the facility become the safest one in America. To achieve its mission, QI initiatives must be implemented to reduce preventable medical errors that result in death.
ORDER A PLAGIARISM FREE PAPER HERE
Analysis of Dashboard Metrics to Identify Quality Issue
Healthcare-associated infections (HCAIs) are infections that are acquired by patients who are receiving treatment in hospitals or healthcare facilities. Additionally, HCAIs appear within 48 hours of hospitalization or within 30 days after receiving care (Haque, Sartelli, McKimm & Bakar, 2018). According to statistics from the U.S Center for Disease Control and Prevention, approximately 1.7 million patients annually acquire HCAIs during treatment and 98,000 of these patients die due to the infections. To reduce the death rate associated with HCAIs, simple infection-control procedures liked hand cleaning with an alcohol-based hand rub have been proven to be effective. Additionally, routine educational interventions for all staff members will help improve hand hygiene practices in healthcare facilities and prevent the spread of infections (Haque et al., 2018). Patients in the ICU are more prone to contracting HCAIs due to reduced host defense mechanisms, non-conformance with infection prevention and control measures, heavy workload on staff and lack of training resulting in cross-contamination and cross-transmission of germs from one patient to the next (Damani, 2015).
According to recent rankings by the Leapfrog Group, a non-profit hospital watchdog institution, Virginia received the second-highest rate of hospital with A ratings for patient safety. However, last on the list with the lowest patient safety rating was VCU Health System which received grade C (Balch, 2019). The ratings by Leapfrog Group are based on public data on the hospitals’ rates of infections, deaths from surgery, patient falls, injuries and other preventable injuries. The C rate that VCU received places the facility at 88 percent greater risk of patients’ death (Balch, 2019).
Table 1: Leapfrog Hospital Safety Grade for VCU Health System
| Infection | MRSA | Clostridium
difficile |
Blood infections | Urinary tract infections | Surgical site infection after colon surgery |
| VCU Score | 0.931 | 1.354 | 0.902 | 0.569 | 0.809 |
| Best hospital’s score | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| Average hospital’s score | 0.881 | 0.751 | 0.765 | 0.831 | 0.860 |
| Worst hospital’s score | 3.352 | 1.940 | 2.943 | 3.010 | 3.067 |
The table above containing scores of VCU’s infection rate was compiled by Leapfrog Hospital safety grade and contributed to its eventual grade of C. The number represents a comparison of the number of infections expected for VCU, given the number of patients they care for on a daily basis and how widespread every infection is in the local community. A number lower than one means that the facility had fewer infections than expected; a number higher than one means that the facility had more infections than expected (Leapfrog Hospital Safety Grade, 2019). Leapfrog Hospital Safety Grade obtained data from hospital survey and CMC. The data that was used to come up with the overall C grade was divided into five categories; infections, problems with surgery, practices to prevent errors, safety problems, doctors, nurses and hospital staff. Overall, VCUHS is facing high HCAIs compared to other medical facilities in the country and compared to acceptable standards.
The center for Adult Critical Care at VCUHS offers 24/7 intensive care services to the critically ill and injured. With over 30 board-certified and fellowship-trained critical care specialists, the Critical Care Hospital serves a majority of residents in Virginia. According to VCUHS 2013 annual report that obtained data from the facility’s clinical dashboard, there was an 86% reduction in healthcare-associated infections in the ICU since 2003 (VCU Medical Center, 2018). However, the rate of HCAIs is still high and the facility is in argent need of a QI initiative to reduce this quality issue.
Table 2: Infections in the ICU
| Year | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 |
| Infections
Per 1,000 Patient days |
22.5 | 17.5 | 12.5 | 10.0 | 7.2 | 6.0 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 2.4 | 2.0 | 2.2 |
Table 2 above highlights the rate of infections in the ICU between 2003 and 2013. According to the table, the facility had an infection rate of 22.5 per 1000 patient days in the year 2003. Over the following years, the number drastically reduced and by 2013, the number reached 2.2 infections per 1000 patient days.
There are four main categories of healthcare associate infection s identified in the data. They include; catheter-associate urinary tract infections (CAUTI), surgical site infections (SSI), ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP) and central line associated bloodstream infection (CLABSI).
Table 3: Rate of Healthcare Associated Infections in the ICU
Table 3 above highlights the rate of healthcare associated infections at VCUs ICU hospital. At 39% CAUTIs are most common HAIs in the facility. This is followed by SSI at 26%, VAP at 18% and CLABSI at 17%.
Table 4: Graph of infection rates per 1000 patient days
The graph above provides a visual presentation of the rate of infections per 1000 patient days. In 2003, VCU had the highest rate of infections in its ICU. However, between 2009 and 2013, the numbers stagnated. This is partly attributed to improved hand hygiene practices among healthcare providers in the facility.
Quality Improvement Initiative Proposal
In line with its mission of being the safest healthcare facility in America, the number of preventable errors must be significantly reduced. In addition to saving lives and improving quality of care for patients, an effective quality improvement initiative will save the facility billions of dollars in damage control after an infection has occurred. The quality improvement initiative for VCU will be based on the rate of Healthcare-associated infections and will use data from the facility’s dashboard regarding the healthcare issue. The QI outline will also identify knowledge gaps, missing information and areas of uncertainty and provide effective solutions to reduce HAIs at VCU.
Outline for the Quality Improvement Initiative
Healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) are increasingly becoming a major patient safety problem in healthcare facilities. With over 1.7 million HAIs and approximately 99,000 healthcare-associated deaths in hospitals, HAIs are a major concern for all stakeholders involved (Mauger et al., 2014). However, considerable progress has been made in identifying preventive strategies and interventions to reduce HAIs. Some of the most preferred strategies include; the use of audits, feedback and provider reminder systems that are in line with the base strategies of organizational change and provider education (Mauger et al., 2014). Considering morbidity and mortality rates, cost implications and the length of stay in the hospital, efforts should be directed towards developing HAI prevention strategies.
Quality Improvement Initiative Proposal
There are several general measures that can be implemented to control infection rates in the ICU. One of the measures is isolation. The need for isolation should be assessed by screening all ICU patients for immunological disorders, diarrhea, skin rashes, communicable diseases or presence of symptoms of an epidemic bacterium (Mehta et al., 2014). After the need for isolation is assessed, the type of isolation needed should be selected. Isolation can either be protective isolation for immunocompromised patients or source isolation for infected patients to control infection transmission to other patients and staff members. Healthcare professionals should also identify patients who are at a higher risk of nosocomial infections. In addition to isolation, healthcare professionals should always observe hand hygiene. Hands are the primary vehicle for the transmission of microorganisms and observing hand hygiene is the most effective way of preventing horizontal transmission of infections within the ICU (Mehta et al., 2014). In line with this realization, VCU should strictly adhere to WHO’s five moments for hand hygiene.
Figure 1: World Health Organization’s Five Moments for Hand Hygiene
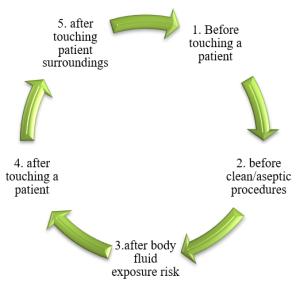
In addition to strictly following the WHO five moments for hand hygiene, healthcare providers should wash their hands with soap and running water after they are visibly soiled with blood or other body fluids. They should also use an alcohol-based hand rub containing 0.5% chlorhexidine and 70% w/v ethanol when their hands are not visibly dirty (Mehta et al. 2014). Regardless of the patient’s status, healthcare professionals should always adhere to standard precautions every time they are in contact with patients in the ICU. Some of the Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) to consider includes sterile gloves, gowns, masks, eye protection equipment, face shields, shoe and head coverings and patient-care equipment. Transmission-based precautions should also be adhered to in addition to standard precautions.
Strategies to reduce ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP)
- Intubation should be avoided whenever necessary
- Use noninvasive ventilation
- Use oral intubations to nasal intubations
- Patient’s head should be elevated at a 30-45-degree angle in a semi-recumbent body position
- Chlorhexidine solution of 0.12% strength should be given orally everyday
- Use endotracheal tubes with subglottic suction port
- Periodic discharge of any condensate in the mechanical ventilator tubing should be regularly checked (Mehta et al. 2014)
Quality Improvement Initiative Proposal
Strategies to reduce Catheter-related bloodstream infection (CRBSI)
- Catheter insertion should be done in the upper extremity
- Before inserting the catheter, skin should be cleaned with more than 0.5% chlorhexidine preparation
- Ultrasound-guided insertion should be used
- Catheter insertion site should be monitored on a daily basis to check if a transparent dressing is present
- Needless intravascular catheter access systems should be used
- Injection ports should be cleaned with appropriate antiseptics (Mehta et al. 2014)
Strategies to reduce urinary tract infection (UTI)
- Catheters should only be inserted for appropriate indications
- Urinary catheter should be aseptically inserted
- A closed drainage system should be maintained
- Maintain unobstructed urine flow
- Catheters that are no longer needed should be removed (Mehta et al. 2014)
Lastly, environmental factors like cleaning and disinfection should be maintained at all times. Patient-care areas should be cleaned and disinfected regularly. Some pathogens like methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) can survive in the environment for longer periods of time. Therefore, EPA-registered disinfectants that are best suited to meet all the needs of the ICU should be used for cleaning and disinfection. The architecture and layout of the ICU should also be considered. The ICU should be situated close to the operating room and emergency department to allow for easy access at all times. Additionally, all air in the ICU should be filtered to approximately 99% efficiency (Mehta et al. 2014). The isolation facility should always have both negative and positive pressure ventilations. Space between beds should be kept and a minimum of 2.5 meters.
All the proposed quality improvement measures to reduce HAIs will not be successful unless the organization’s management offers its support. Therefore, the QI implementation team should work closely with the hospital’s management and lobby for a better patient to nurse ratio in the ICU. Likewise, policies for controlling traffic flow in the ICU should be implemented to reduce possible sources of contamination from staff members, equipment and visitors (Mehta et al 2014). Education and training should be offered to all ICU staff to help improve their knowledge on nosocomial infections. Antibiotic stewardship and vaccination of ICU healthcare personnel should be adhered to.
The aforementioned quality improvement strategies will only be effective if an interprofessional approach is taken. Therefore, the next stage of the proposal will integrate interprofessional perspectives to lead quality improvement in patients.
Interprofessional Perspectives to Support Quality Improvement
Patients have complex health needs and often require several disciplines to address their health issues. According to recommendations by the Institute of Medicine Committee on Quality of Health Care in America, all healthcare professionals should work in interprofessional teams to best address the complex needs of patients (Bridges et al. 2014). By working in teams, healthcare professionals are able to share expertise and unique perspectives to form a common goal of restoring health and improving patient outcomes. The success of interprofessional teams is based on several assumptions including; interprofessional team members see their roles as important to the team, all healthcare professionals’ value patient safety and work towards observing quality standards, there is open communication among team members, there is existence of autonomy and equality in resource sharing (Bridges et al. 2014).
Based on the assumption that interprofessional team members see their roles as important, the organization’s leadership should be at the forefront in infection control and prevention. Leadership plays an important role in the implementation of guideline recommendations and organizing for training and education activities (Hegarty et al. 2018). By demonstrating tangible support to teams, ensuring that resources are available to facilitate change and hiring healthcare practitioners, leadership facilitates quality improvement in the organization. In their role as facilitators, organization’s leaders guide the implementation of standards, strategic approaches and the principles of bottom-up working. In line with this, VCU leadership has a crucial role to play to reduce the rate of healthcare-associated infections in the facility. By contributing to infection prevention actions and by implementing guidelines, the hospital’s leadership facilitates the QI process. Leadership should also listen to workforce concerns, motivate and engage healthcare workers, acknowledge when staff members are stressed and overstretched, overcome challenges that HAIs prevention strategies face and promote collaboration across all disciplines (Hegarty et al., 2018).
Quality Improvement Initiative Proposal
Effective Communication Strategies to Promote Quality Improvement
Effective communication is crucial to the success of all quality improvement initiatives. In line with this assumption, VCU should design a communication strategy that engages every staff member in the ICU, promotes awareness and understanding of all the QI interventions proposed to reduce the rate of HCAIs in the ICU hospital (Cooper et al., 2015). Overall, systematic and structured communication strategies enhance quality improvement initiatives.
In line with the assumption that all healthcare providers value patient safety and strive to observe quality standards, healthcare workers as members of interprofessional teams have a crucial role to play in the reduction of HCAIs (Shah & Holmes, 2015). Understanding healthcare worker’s behavior is critical to develop effective behavior change interventions. Studies show that HCAIs are mainly caused by healthcare workers who are not compliant with IPC practices. This behavior is often attributed to a lack of effective communication, environmental circumstances, duties and social circumstances. To reduce non-compliance rates among ICU staff members, VNU should analyze the hierarchy of influence in traditional clinical roles that challenge work relationships. Additionally, the facility should prioritize risk appraisals to remove any and all divergence in values attached to its policies and practices (Shah & Holmes, 2015). Lastly, the facility should remove ambiguities surrounding healthcare workers’ duties and responsibilities.
Quality Improvement Initiative Proposal
Conclusion
For healthcare organizations like VCU Medical Center, maintaining quality is of the upmost importance. Thus, when there are quality-related issues like increased rates of HCAIs in the ICU department, the facility should immediately implement a quality improvement initiative that will address the safety issue and improve overall performance of the facility. Effective quality improvement initiatives should have interprofessional perspectives imbedded in them and effective communication strategies that ensure that communicate the QI goals and objectives to all the stakeholders involved. While QI initiatives are designed to control quality-related issues, they have little chance of success if the organization’s management does not support them.
References
Balch, B. (2019). Hospital Safety Report: Virginia Ranks Second Best in Nation: VCU, Southside Regional Lag with C Grade. Richmond Times-Dispatch. Retrieved from https://www.google.com/amp/s/www.richmond.com/hospital-safety-report-virginia-ranks-second-best-in-nation-vcu/article.amp.html
Bridges, D.R., Davidson, R.A., Odegard, P.S., Maki, I.V & Tomkowiak, J. (2014). Interprofessional Collaboration: Three Best Practice Models of Interprofessional Education. Medical Education Online, 16. Doi: 10.3402/meo.v16i0.6035
Cooper, A., Gray, J., Willson, A. et al (2015). Exploring the Role of Communications in Quality Improvement: A Case Study of the 1000 Lives Campaign in NHS Wales. Journal of Communication in Healthcare, 8(1), 76-84. Doi: 10.1179/1753807615Y.000000000000006
Damani, N. (2015). Healthcare-associated Infections in Intensive Care Units: Epidemiology and Infection Control in Low-to-middle Income Countries. J Infect Dev Ctries, 9(10), 1040-1045. Doi: 10.3855/jidc.6832
Haque, M., Sartelli, M., McKimm, J. & Bakar, M. (2018). Health Care-Associated Infections- an Overview. Infection and Drug Resistance, 11, 2321-2333. Doi: 10.2147/IDR.S177247
Hegarty, J., Murphy, S. et al. (2018). Leadership Perspectives on the Implementation of Guidelines on Healthcare-associated Infections. BMJ Leader, 3(2). Doi: 10.1136/leader-2018-000111
Mauger, B., Marbella, A., Pines, E., Chopra, R., Black, E.R & Aronson, N. (2014). Implementing Quality Improvement Strategies to Reduce Healthcare-associated Infections: A Systematic Review. American Journal of Infection Control, 42, S274-S283. Doi: 10.1016/j.ajic.2014.05.031
Mehta, Y., Gupta, A., Todi, S., Myatra, S.N. et al. (2014). Guidelines for Prevention of Hospital Acquired Infections. Indian Journal of Critical Care Medicine: Peer-reviewed, Official Publication of Indian Society of Critical Care Medicine, 18(3), 149-163. Doi: 10.4103/0972-5229.128705
Shah, N. & Holmes, A.H. (2015). Towards Changing Healthcare Workers’ Behavior: a Qualitative Study Exploring non-Compliance through Appraisals of Infection Prevention and Control Practices. Journal of Hospital infection, 90(2), 126-134. Doi: 10.1016/j.jhin.2015.01.023
VCUHealth. (2019). Our Story. Retrieved from https://www.vcuhealth.org/our-story/our-story
VCU Medical Center. (2018). 2013 Annual Report. Retrieved from https://annualreports.vcu.edu/archive/medical/2013/stories/safetyfirst.html
White, M., Butterworth, T. & Wells, J.S. (2017). Healthcare Quality Improvement and Work Engagement: Concluding Results from a National, Longitudinal, Cross-sectional Study of Productive Ward-Releasing Time to Care Programme, BMC Health Services Research, 17, 510. Doi: 10.1186/s12913-017-2446-2
Needs help with similar assignment?
We are available 24x7 to deliver the best services and assignment ready within 3-4 hours? Order a custom-written, plagiarism-free paper

